
Abstract:The difluoromethylene (CF₂) group, valued for its unique electronic and steric properties, plays a critical role in pharmaceutical and agrochemical design, as exemplified by drugs like lubiprostone, which requires ethyl 2,2-difluorohexanoate as a key intermediate for its synthesis. Consequently, developing efficient methods to incorporate the ethoxycarbonyldifluoromethyl group into alkanes is highly desirable. Herein, we describe a mild, versatile, and efficient radical hydro-ethoxycarbonyldifluoromethylation of alkenes with BrCF2CO2Et. This process is applicable to both unactivated alkyl alkenes and active aryl alkenes. The protocol is characterized by mild reaction conditions, the absence of expensive reagents, and the elimination of transition metals.


Abstract:The cyanodifluoromethyl group (−CF2CN) has emerged as a valuable fluorinated motif, with growing recognition for its potential applications in medicinal chemistry and materials science. However, its efficient incorporation into organic compounds remains a synthetic challenge. Herein, we report a copper-promoted reductive cross-coupling protocol for the cyanodifluoromethylation of (hetero)aryl iodides using bromodifluoroacetonitrile (BrCF2CN) as a cost-effective and readily available reagent. This method demonstrates broad substrate compatibility, delivering target products in moderate to good yields under mild and operationally simple conditions. Successful gram-scale synthesis and late-stage functionalization of complex molecules further highlight the utility of the protocol.


Abstract:A one-pot transformation of aliphatic and aromatic tertiary amines to novel fluorinated enaminones has been developed, utilizing perfluoroalkyl ether carboxylates (PFECA salts) featuring “–CF2O–” units as the fluorine-containing reagents. Carbonyl fluoride, acyl fluorides and anhydrides by thermal decomposition of these PFECA salts were proposed to act as key active species that trigger the tandem oxidation–acylation process of tertiary amines, through enamine intermediates.


Abstract:The defluorination of trifluoromethyl groups typically involves breaking one or all three C–F bonds, while selectively cleaving exactly two C–F bonds presents a considerable challenge. In this work, we present a method for the sequential defluorination of trifluoromethyl hydrazones under photocatalytic conditions, which involves the specific breakage of two C–F bonds followed by thiolation to yield monofluorinated alkenes containing a thiol group. Transforming trifluoromethyl-containing polyfluoroalkyl substances into fluorinated non-PFAS compounds holds potential practical implications.




Abstract:Current radiopharmaceuticals for treating bone metastatic tumors have various limitations. We focus on developing a universal, economical, efficient, and safe novel radiopharmaceutical for bone metastasis treatment. 131I is a well-established medical radionuclide commonly used for both treatment and diagnosis. Risedronate exhibits strong bone-targeting properties with moderate bone retention. This study explored the combination of these two components and evaluated its biological properties in animal experiments. Based on the experimental results, 131I-risedronate demonstrated high bone-targeting efficiency, low uptake in nontarget organs, and rapid clearance. Notably, at 3 days postadministration, significant bone retention was observed, indicating its potential for sustained therapeutic effects. Additionally, its biodistribution and therapeutic effect can be effectively monitored by SPECT/CT imaging.


Abstract:Fluoroether approach has been extensively employed as an alternative to conventional fluorinated surfactants; however, it faces challenges such as inadequate performance of short fluoroether chains and environmental contamination from long fluoroether chains. This study aims to address the conflict between environmental compatibility and the performance of fluoroether surfactants. The design of the surfactants is centered around the OC chain (CF3(OCF2)n–), utilizing reduced fluorine content to achieve superior surface activity. A series of surfactant molecules featuring elongated hydrophobic chains and dual-chain structures have been synthesized and characterized. All of the molecules have good surface activity at low concentrations. Among them, CF3(OCF2)4CH2O(CH2)3SO2NH(CH2)3N(CH+3)2CH2COO– (OC4F-B), which employs a strategy of extending the hydrophobic chain by insertion of –CH2O(CH2)3–, shows the best performance. This surfactant can achieve a surface tension of 20 mN/m at a concentration of 0.005 wt %, which is 20 times lower than that required for CF3(OCF2)4CONH(CH2)3N(CH+3)2CH2COO– (OC4-betaine) to attain the same surface tension. In contrast, (CF3(OCF2)3CH2O(CH2)3SO2NHCH2CH2)2N(CH+3)CH2COO– (DOC3F-B), utilizing both dual-chain and extended carbon chain strategies, exhibits a critical micelle concentration that is diminished by 2 orders of magnitude relative to OC3-betaine, reaching to 0.047 g/L. Merely adjusting the length of the fluorocarbon chain is insufficient to reconcile the conflict between the performance and environmental impact of fluorinated surfactants. This study introduces an innovative approach by incorporating hydrocarbon hydrophobic chains and adopting a dual-chain design, thereby addressing this challengeeffectively.


Abstract
Aim: Diabetes-associated cognitive impairment (DACI) is a common complication of Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), with its mechanisms and treatments for DACI remaining incompletely clarified. This study investigated the protective efficacy of the novel lipid S-enantiomer of 9-palmitic acid esters of hydroxy stearic acids (S-9-PAHSA, S9P) in a high-fat diet-induced DACI mouse model.
Methods: Mice were randomly assigned to three groups: normal diet (ND), high-fat diet (HFD), and HFD + 30 mg/kg/day S9P (HFD + S9P). Fasting blood glucose (FBG), intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT), and insulin tolerance test (ITT) were conducted to assess blood glucose homeostasis. Morris Water Maze and Y maze tests evaluated cognitive function, and neuronal status was examined through pathological analysis, Golgi staining, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Colonic barrier integrity was assessed using periodic acid-Schiff and Alcian blue staining (AB-PAS) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining. Intestinal microbiota composition was analyzed by 16S rDNA sequencing, and serum metabolic characteristics were determined by metabolomics sequencing.
Results: S9P improved glucose homeostasis and alleviated cognitive decline in DACI mice. It also mitigated neuronal damage, dendritic degeneration, and synaptic damage, while restoring colonic barrier integrity and ameliorating gut microbiome imbalances, insulin resistance, and lipid imbalance. Additionally, S9P regulated metabolite profiles and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways, and reduced astrocyte activation and neuroinflammatory responses in the hippocampus of HFD-induced DACI mice.
Conclusion: S9P had a protective effect against HFD-induced diabetic cognitive impairment closely related to the modulation of the gut-brain axis, suggesting that S9P has the potential to become a new therapeutic approach for DACI.

Abstract:A protocol was developed for the large-scale preparation (nearly 200 g per batch) of (CF3S)2C═S. The synthesis of gem-bis(trifluoromethylthio)alkenes was achieved through the Barton–Kellogg reaction, without the involvement of trivalent phosphines. With slight modifications to the reaction conditions, the synthesis of gem-bis(trifluoromethylthio)cyclopropanes, which are difficult to obtain by other methods, can be realized. Due to the large steric hindrance of the trifluoromethylthio group, the CF3S group may be positioned close to the trans-substituent rather than the cis-substituent in cyclopropanes, as confirmed by single-crystal X-ray analysis, contributing to unique NMR structural characteristics. Further investigation into the reaction mechanism revealed the unique reactivity of the double bond in gem-bis(trifluoromethylthio)alkenes.


Abstract:Considering the unique electronic properties of the CF2 and the CN groups, the CF2CN group has significant potential in drug and agrochemical development, as well as material sciences. However, incorporating a CF2CN group remains a considerable challenge. In this work, we disclose a use of bromodifluoroacetonitrile (BrCF2CN), a cost-effective and readily available reagent, as a radical source for cyanodifluoromethylation of alkyl alkenes, aryl alkenes, alkynes, and (hetero)arenes under photocatalytic conditions. This protocol demonstrates an exceptionally broad substrate scope and remarkable tolerance to various functional groups. Notably, the cyanodifluoromethylation of alkynes predominantly provides sterically hindered alkenes, a thermodynamically unfavorable outcome, and (hetero)arene C-H bonds are directly amenable to cyanodifluoromethylation without pre-functionalization.


Abstract:Reductive deoxygenation of alcohols is particularly challenging because of the high bond dissociation energy of the C–OH bond and the poor leaving ability of the hydroxyl group. Herein we describe a Ph3P═O-catalyzed reductive deoxygenation of benzyl alcohols with PhSiH3 under an air atmosphere within 30 min of reaction time. The use of catalytic loading of Ph3P═O enhances the practicality of this protocol.


Abstract:Although the desulfurization of thiols is a topic of great importance and has received significant attention, most efforts have focused on the hydrodesulfurization of thiols. In this work, we describe the desulfurization of thiols for nucleophilic substitution. This process occurs rapidly, promoted by the Ph3P/ICH2CH2I system, and can be extended to a wide range of nucleophiles. Notably, free amines can be employed as nucleophiles to synthesize various secondary and tertiary amines. This method tolerates a wide array of functional groups, including hydroxyl groups in amination reactions. Benzyl thiols are particularly reactive and can be completely converted at room temperature within 15 min. Although alkyl thiols show lower reactivity, they can also be converted smoothly at a reaction temperature of 70 °C overnight.


Abstract: Efforts to develop alternatives to triflic anhydride (Tf2O) as a trifluoromethylation reagent continue due to its limitations, including volatility, corrosiveness, and moisture sensitivity. Described herein is the use of a trifluoromethylsulfonylpyridinium salt (TFSP), easily obtained by a one-step reaction of Tf2O with 4-dimethylaminopyridine, as a reagent for the trifluoromethylative difunctionalization of alkenes by photoredox catalysis. DMSO and CH3CN are suitable solvents for achieving keto- and amino-trifluoromethylation of alkenes, respectively, with good functional group tolerance.


Abstract: With the rapidly increasing prevalence of metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), neuronal complications associated with these diseases have resulted in significant burdens on healthcare systems. Meanwhile, effective therapies have remained insufficient. A novel fatty acid called S-9-PAHSA has been reported to provide metabolic benefits in T2DM by regulating glucose metabolism. However, whether S-9-PAHSA has a neuroprotective effect in mouse models of T2DM remains unclear.


Abstract: Ph3P+CF2CO2– (PDFA), a reagent that was developed by us recently, has found widespread applications in the synthesis of fluorinated molecules. Its great synthetic potential stimulates us to develop an effective synthetic route on a kilogram scale, which is described in this work. The used reagents are all cheap and easily available. We also demonstrate that the aldehyde group is significantly more reactive than the double bond group toward PDFA even though both of these two groups are very reactive toward PDFA.



Abstract: Difluorocarbene has found widespread applications in the synthesis of fluorine-containing molecules. We have previously found that difluorocarbene can react with elemental sulfur to produce thiocarbonyl fluoride, which is of great value for the new discoveries of difluorocarbene chemistry and the investigations of synthetic utilities of thiocarbonyl fluoride. We have developed the transformation of difluorocarbene into thiocarbonyl fluoride as a synthetic tool to achieve trifluoromethylthiolation of terminal alkynes and alkyl halides. In continuation of our research interest in this chemistry, herein we further apply the difluorocarbene transformation to the trifluoromethylthiolation of aryl and alkenyl iodides. Trifluoromethylthiolation is an active research area in organofluorine chemistry, and the commonly used trifluoromethylthiolation methods usually require the use of expensive CF3S-containing reagents. In contrast, in our protocol the CF3S group is generated in situ from difluorocarbene, elemental sulfur and a fluoride anion, all of which are cheap and easily available reagents. The general experimental procedure is shown as follows. Into a 5 mL sealed tube were added 4-phenyl phenyl iodide (1a, 56.0 mg, 0.2 mmol), S (57.8 mg, 1.8 mmol), Ph3P+CF2CO2– (PDFA) (213.8 mg, 0.6 mmol), AgF (0.5 mmol, 63.4 mg), ligand L1 (0.6 mmol, 158.9 mg), CuI (76.2 mg, 0.4 mmol), and dioxane (1.0 mL) under a N2 atmosphere. The reaction mixture was stirred at 110 ℃ for 8 h. After the reaction system was cooled to room temperature, Et3N (0.5 mL) was added to remove the excess elemental sulfur by a redox reaction (the final product would be contaminated by elemental sulfur if elemental sulfur was not removed). The mixture was diluted with 10 mL of saturated brine, and then the product was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated to 1 mL. The residue was subjected to flash column chromatography to afford the pure product.


Abstract: Difluorocarbene has served as a versatile intermediate for the incorporation of fluorinated groups into organic molecules. Extensive studies have shown that difluorocarbene can act as a CF2 source and a nonfluorinated C1 source. However, the use of difluorocarbene as a C–F source remains a challenging task. Herein we disclose that difluorocarbene can function as a C–F source for the cyclization of 2-aminobenzenethiols, allowing for the construction of fluorinated benzothiazoles, which may provide new possibilities for drug developments due to the magic effects of the fluorine element and the pharmacological properties of benzothiazoles.


Abstract: Fenofibrate is known as a lipid-lowering drug. Although previous studies have reported that fenofibrate exhibits potential antitumor activities, IC50 values of fenofibrate could be as high as 200 μM. Therefore, we investigated the antitumor activities of six synthesized fenofibrate derivatives. We discovered that one compound, SIOC-XJC-SF02, showed significant antiproliferative activity on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) HCCLM3 cells and HepG2 cells (the IC50 values were 4.011 μM and 10.908 μM, respectively). We also found this compound could inhibit the migration of human HCC cells. Transmission electron microscope and flow cytometry assays demonstrated that this compound could induce apoptosis of human HCC cells. The potential binding sites of this compound acting on human HCC cells were identified by mass spectrometry-cellular thermal shift assay (MS-CETSA). Molecular docking, Western blot, and enzyme activity assay-validated binding sites in human HCC cells. The results showed that fumarate hydratase may be a potential binding site of this compound, exerting antitumor effects. A xenograft model in nude mice demonstrated the anti-liver cancer activity and the mechanism of action of this compound. These findings indicated that the antitumor effect of this compound may act via activating fumarate hydratase, and this compound may be a promising antitumor candidate for further investigation.


Abstract: Owing to the ubiquity of the hydroxyl group, reductive deoxygenation of alcohols has become an active research area. The classic Barton–McCombie reaction suffers from a tedious two-step procedure. New efficient methods have been developed, but they have some limitations, such as a narrow substrate scope and the use of moisture-sensitive Lewis acids. In this work, we describe the Ph3P/ICH2CH2I-promoted reductive deoxygenation of alcohols with NaBH4. The process is applicable to benzyl, allyl and propargyl alcohols, and also to primary and secondary alcohols, demonstrating a wide substrate scope and a good level of functional group tolerance. This protocol features convenient operation and low cost of all reagents.


Abstract: Difluorocarbene has served as a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. The transformation of difluorocarbene into thiocarbonyl fluoride, which was discovered by us previously, can be developed as a synthetic toolfor the cyclization of vicinal X-H substituted amines to provide various five-membered heterocycles. However,aryl amines are required to be used and difluoromethylation of the N–H bond or a newly generated S-H bondcannot be suppressed. Herein we describe the use of thiocarbonyl fluoride generated in situ as a thiocarbonylsource for the cyclization of vicinal X-H substituted alkyl amines (X = N, O, S) to provide imidazolidine-2-thiones, oxazolidine-2-thiones and thiazolidine-2-thiones. The use of alkyl amines constructs different heterocycles with those obtained from aryl amines. The free N–H bond remains intact without beingdifluoromethylated.


Abstract: Due to its unique electronic properties, the difluoromethylene group (CF2) has served as a valuable unity in the design of biologically active molecules. Since γ-lactones display a broad range of biological properties, α,α-difluoro-γ-lactones may exhibit unexpected biological activities, and thus their synthesis has received increasing attention. Traditional synthetic methods suffer from tedious multi- step processes, and very few effective methods have been reported recently. Herein, we describe the difunctionalization of alkenes with BrCF2CO2K under photoredox catalysis with the use of a boron-Lewis acid for the access to α,α-difluoro-γ-lactones. In this transformation, the alkene substrates and the used reagents, including BrCF2CO2K and the boron-Lewis acid, PhB(OH)2 or BF3·THF, are cheap and widely available. High efficiency and atom economy may make this protocol attractive.


Abstract: Described here is the R3P/ICH2CH2I-promoted dehydroxylative sulfonylation of alcohols with a variety of sulfinates. In contrast to previous dehydroxylative sulfonylation methods, which are usually limited to active alcohols, such as benzyl, allyl, and propargyl alcohols, our protocol can be extended to both active and inactive alcohols (alkyl alcohols). Various sulfonyl groups can be incorporated, such as CF3SO2 and HCF2SO2, which are fluorinated groups of interest in pharmaceutical chemistry and the installation of which has received increasing attention. Notably, all reagents are cheap and widely available, and moderate to high yields were obtained within 15 min of reaction time.


Abstract: A Ph3P/ICH2CH2I-promoted dehydroxylative cyanation of alcohols avoids the use of transition metals or moisture-sensitive Lewis acids. This protocol features convenient operations, mild reaction conditions, and the use of cheap and widely available reagents.


Abstract: Described herein is the convenient synthesis of an efficient trifluoromethoxylation reagent, nC4F9SO3CF3, by using cheap and widely available reagents and without the need of any tedious column chromatography purification procedure.


Abstract: Depending on the nature of the attached functional moiety, the sulfonyl radical can either undergo an automatic SO2 liberation or react directly as the thermodynamically favored sulfonyl radical. Taking advantage of this unique property, we envisioned that through rational reaction design, the in situ release and re-insertion of SO2, i. e., the shuttle of SO2, can be realized. Herein we report our recent progress in copper metallaphotoredox co-catalyzed trifluoromethyl-fluorosulfonylation of alkenes with TFSP as both the CF3 and SO2 source. Valuable functional groups are added across the double bonds. Besides, A wide array of synthetically useful moieties featuring distinct electronic patterns and various nitrogenous heterocycles are well tolerated by this strategy.


Abstract: Cyanex923 (a mixture of four trialkyl (hexyl and octyl) phosphine oxides) has been extensively employed in the recovery of cerium (Ce(IV)) and fluorine (F), as well as the separation over thorium (Th(IV)) from bastnaesite. However, rigorous production conditions and involvement of highly toxic raw materials (PH3) have been critical problems to be solved during the synthesis of Cyanex923. Meanwhile, its extraction performance remains to be improved. Therefore, we attempted to adjust the feed ratio to increase the proportion of short carbon chain components, successfully synthesized a novel extractant (P113, a mixture of four trialkyl (hexyl and octyl) phosphine oxides) with contents of each component different from Cyanex923 using an environmentally benign method. The comparison with Cyanex923 revealed obvious improvement of P113 in terms of extraction efficiency, selectivity and saturation capacity. The extraction efficiency and saturation capacity of Ce(IV) were increased by 10% and 10 g L-1, respectively. Separation factor of Ce(IV)/Th(IV) was increased from 16 to 27 at 2 mol L-1 H2SO4. Furthermore, P113 presented excellent regenerability. The superiority of P113 was theoretically explored using the density functional theory (DFT) and polarizable continuum model (PCM), and the results indicated that THPO (trihexyl phosphine oxide) had lower extraction phase transfer energy than TOPO (trioctyl phosphine oxide) from aqueous phase to organic phase. The comprehensive evaluation of P113 demonstrated the feasibility employed in the recovery of Ce(IV)-F and the separation of Th(IV) from bastnaesite, which advanced industrial application of the novel extractant, and held significant value for the utilization of resources and environmental protection.





Abstract: Herein, we describe the design and synthesis of a difluoromethylsulfonyl imidazolium salt, which can act as a radical difluoromethylation reagent to achieve the challenging amino- and oxy-difluoromethylation of alkenes. Notably, the three steps for the synthesis of the imidazolium salt do not require any tedious distillation or column chromatography purification process, and the amino- and oxy-difluoromethylation paths are simply determined by the selection of reaction solvents.


Abstract: The trifluoromethylsulfonyl pyridinium salt (TFSP) was used as a CF3S source for the trifluoromethylthiolation of indole derivatives. It is proposed that TFSP is reduced in the presence of diethyl phosphite and NaCl. The protocol features a facile access to the CF3S source, and high efficiency and transition-metal free conditions for trifluoromethylthiolation.


Abstract: A successful Cu-catalyzed addition of both Cl and SO2OCF2H groups into alkenes allows us to discover the unusual reactivity of the SO2OCF2H group. As opposed to common sulfonic esters (RSO2-O-R′), in which the R′ group is highly electrophilic, the SO2 moiety demonstrates higher electrophilicity in RSO2–OCF2H. The unexpected reactivity is further developed not only as a synthetic tool for well-functionalized alkenyl sulfonyl fluorides but also for the first 18F labeling of alkenyl sulfonyl fluorides.


Abstract: Tetraphenylporphyriyne (Pyne1), a novel porphyrin analogue with a C≡C bond incorporated into an 18-π-conjugated system, has been created via cleavage of the N-confused pyrrolic ring in Ag(III) N-confused tetraphenylporphyrin. The structure of Pyne1 was confirmed by X-ray crystallography and 1H NMR, IR, and UV–vis spectroscopy. The mechanism of cleavage of the N-confused pyrrolic ring was investigated by theoretical calculations. The successful synthesis of other Pynes indicated the generality of this protocol.


Abstract: The fluorination of alkenes with electrophilic N−F type reagents usually occurs through a Markovnikov-type addition, and the anti-Markovnikov-type addition may require the use of a transition metal catalyst or an expensive catalyst. Herein we describe a convenient anti-Markovnikov iodofluorination of alkenes with Selectfluor/nBu4NI. A wide substrate scope and good functional group tolerance were observed. The process allows for the construction of various C−F bonds, especially tertiary C−F bonds. The remarkable features make this protocol attractive, including convenient operations, simple reaction conditions, and the installation of an iodine atom which provides possibilities for further transformations.


Abstract: A protocol for visible light mediated C–H trifluoromethylation of unactivated (hetero)arenes under blue LED irradiation has been developed. The reaction enables the rapid construction of a range of CF3-containing (hetero)arenes in moderate to high yields from the readily accessible trifluoromethylsulfonyl-pyridinium salt (TFSP). This protocol is also suitable for nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycles, which are potentially useful in medicinal chemistry.


Abstract: Heptafluoroisopropylthio group (-SCF(CF3)2) has bioactivities in insecticidal molecules, but the protocol for direct introduction of -SCF(CF3)2 is under-explored. Described here is a protocol on heptafluoroisopropylthiolation of benzyl halides with a hexafluoropropylene (HFP)/CsF/S8 system. The reaction enables the rapid construction of a range of (CF3)2CFS-containing compounds from readily available materials. This protocol may find application in the synthesis of (CF3)2CFS-containing biologically active molecules.

159.Zhu,Yu-Rong;Lin,Jin-Hong*;Xiao,Ji-Chang*.“Triphenylphosphine/1,2-Diiodoethane-Promoted Formylation of Indoles with N,N -Dimethylformamide” Synlett 2022, 33, 259-263.2021.10.20
DOI: 10.1055/a-1675-1043
Highlights in Organic Chemistry

Abstract: Despite intensive studies on the synthesis of 3-formylindoles, it is still highly desirable to develop efficient methods for the formylation of indoles, due to the shortcomings of the reported methods, such as inconvenient operations and/or harsh reaction conditions. Here, we describe a Ph3P/ICH2CH2I-promoted formylation of indoles with DMF under mild conditions. A Vilsmeier-type intermediate is readily formed from DMF promoted by the Ph3P/ICH2CH2I system. A one-step formylation process can be applied to various electron-rich indoles, but a hydrolysis needs to be carried out as a second step in the case of electron-deficient indoles. Convenient operations make this protocol attractive.




Abstract: In contrast with unactivated alkenes, the corresponding hydrotrifluoromethylation of styrene has remained challenging due to the strong propensity of styrene for oligomerization and polymerization. On the basis of our newly developed trifluoromethylation reagent, TFSP, herein we present a general method for the hydrotrifluoromethylation of styrene under photoredox catalysis. The substrate scope was further extended to unactivated alkenes, acrylates, acrylamides, and vinyl-heteroatom-substituted alkenes. The tunability of this method was showcased via the relevant deprotonative trifluoromethylation and trifluoromethyltrifluoroethoxylation reactions.


Abstract: Nuclear-pure grade 7LiF was prepared by fluorination reaction of 7LiOH·H2O with electronic grade hydrofluoric acid, and various preparation process conditions were studied. The effects of the concentration and adding amounts of hydrofluoric acid, reaction temperature, reaction time, aging time and drying temperature on the quality and yield of 7LiF were screened and optimized preparation condition of 7LiF was established. Firstly, 20.00g of 7LiOH·H2O was added into the hydrofluoric acid with a mass concentration of 20% and a molar ratio of 1. 1. Then, the mixture was stirred at 80℃ for 2 h, and followed by being aged for 10 h. After that, it was filtered, washed, and then dried in vacuum at 130℃ for 20 h. Finally, the nuclear-pure grade 7LiF was obtained with a high yield of ≥ 99.0%, a Purity ≥ 99.98% and a total oxygen content of ≤0.20%. As the quality index of 7LiF meets the requirements of molten salt preparation raw materials for molten salt reactors, our research provides key raw material and technical support for the large-scale preparation and application of fluoride molten salt (7LiF-BeF2) for the fourth-generation advanced nuclear power reactor.


Abstract: 7LiF is the basic raw material for preparing molten salt coolant 7LiF-BeF2, and its impurity content is directly related to the purity and application performance of molten salt. A new method for the determination of impurity oxygen content in 7LiF for molten salt reactor was developed by inert gas fusing-infrared absorption method. The effects of different fluxes and heating power on oxygen content in 7LiF were investigated, and a better method for the determination of oxygen content in 7LiF was found. The relative standard deviation of oxygen is 2.9% and the recoveries are 99.9-107%, under the condition of 2200W analytical power, silver boat as flux and 0.1g sample weight. The results show that the method is easy to operate and fast, and can meet the quality control requirements in the production process of 7LIF, which provides a strong technical support for the large-scale preparation of 7LiF for the fourth generation of advanced nuclear power reactors.


Abstract: Herein we describe an efficient construction of HCF2Se and HCF2S groups by tandem substitutions between alkyl bromides and a reagent system consisting of MSeCN (or MSCN) and Ph3P+CF2H Br–. The tandem process occurs via the first nucleophilic substitution of alkyl bromides by −SeCN (or −SCN) and the subsequent nucleophilic difluoromethylation.


Abstract:Trifluoromethyl substitution is notably popular in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals; however, trifluoromethylated compounds normally rely on the use of cost-prohibitive or gaseous trifluoromethylating reagents, which diminishes the general applicability of these methods. Herein an efficient trifluoromethylation reagent trifluoromethylsulfonyl–pyridinium salt (TFSP) was reported, which can be readily prepared from cheap and easily available bulk industrial feedstocks. TFSP can generate a trifluoromethyl radical under photocatalysis and realize the effective azido- or cyano-trifluoromethylation reactions of alkenes.


Abstract: Fluorinated molecules have a wide range of applications and are used as medicines, agrochemicals and refrigerants and in smartphone liquid crystal displays, photovoltaic solar cells, Teflon tapes and the coatings of textiles and buildings. Fluorination and fluoroalkylation — incorporation of a trifluoromethyl, difluoromethyl or monofluoromethyl group — are the major strategies used for the construction of carbon–fluorine bonds and fluorinated carbon–carbon bonds, respectively. The past two decades have witnessed a rapid growth in fluorination and fluoroalkylation methods thanks to the development of new reagents and catalysts. This Primer aims to provide an overview of state-of-the-art strategies in fluorination, trifluoromethylation, difluoromethylation and monofluoromethylation, with an emphasis on using C–H functionalization, although other strategies for fluorination and fluoroalkylation are also discussed. Further landmark achievements are expected in the fields of fluorination and fluoroalkylation as organofluorine compounds are used increasingly in everyday applications.


Abstract:Although transition metal carbenes have found widespread applications and difluorocarbene has served as a versatile intermediate, it is still quite challenging to make use of transition-metal difluorocarbenes in synthetic chemistry due to their unpredictable reactivities. In this Highlight, we review recent developments in the transition-metal-catalyzed or -mediated transfer of difluorocarbene and the reactivies and conversions of transition-metal difluorocarbene complexes. We start with the M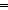 CF2 bonding, then provide the progress in the transfer of difluorocarbene, and finally briefly discuss the conversions of M
CF2 bonding, then provide the progress in the transfer of difluorocarbene, and finally briefly discuss the conversions of M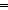 CF2 into other metal complexes. The understanding of the interesting reactivities of M
CF2 into other metal complexes. The understanding of the interesting reactivities of M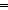 CF2 may help design the catalytic transfer of difluorocarbene for various reactions.
CF2 may help design the catalytic transfer of difluorocarbene for various reactions.


Abstract: Described herein is a Rh-catalyzed tunable defluorinative borylation of allylic gem-difluorides to provide allylborylated monofluoroalkenes or homoallylborylated monofluoroalkenes with excellent Z/E selectivities. Completely different reaction paths were observed by slightly changing the reaction conditions. Allylborylated monofluoroalkenes were further converted into dihydroxyl-containing monofluoroalkenes.


Abstract: The installation of a HCF2 group is a research area that has received increasing attention, and deoxydifluorination of aldehydes have served as an attractive protocol due to the wide availability of aldehydes. Herein we describe a Ph2S/Selectfluor-promoted deoxydifluorination of aldehydes under mild conditions. Compared with previous deoxydifluorination methods, which usually use hazardous reagents such as SF4, DAST and Deoxo-Fluor, this protocol is quite attractive because of the safe and convenient operations, and the use of easily available reagents.


Highlighted by P. Jubault, et al. (Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of 1,2-trans-Disubstituted PhSO2CF2-containing Cyclopropanes. Adv. Synth. Catal.
Abstract: CF3‐ or HCF2‐substituted cyclopropanes are of great interest in pharmaceutical chemistry and agrochemistry, and thus significant efforts have been directed towards the development of efficient methods for the installation of these motifs. This Minireview summarizes recent efforts for the construction of CF3‐ or HCF2‐substituted cyclopropanes. CF3‐cyclopropanes are usually synthesized by a transition‐metal‐catalyzed cyclopropanation of alkenes with a trifluoromethylcarbene generated in situ from a diazocompound, CF3CHN2 or CF3C(Ar)N2. The synthesis of HCF2‐cyclopropanes remains largely unexplored. Some difluoromethylcarbene reagents have been developed, such as HCF2CHN2, Ph2S+CH2CF2H TfO−, and difluoroacetaldehyde N‐triftosylhydrazone (DFHZ‐Tfs), and cyclopropanation of alkenes with these reagents could also occur by transition metal catalysis. These protocols may find great utility in the synthesis of biologically active molecules.


Abstract: Although cyanofluoroalkylation has received increasing attention, a toxic cyanation reagent is usually required. Herein, a Cu-catalyzed difluorocarbene-based cyanodifluoromethylation of alkenes with BrCF2CO2Et/NH4HCO3 under photocatalytic conditions is described. BrCF2CO2Et and NH4HCO3 serve as a carbon source and a nitrogen source of the nitrile group, respectively, avoiding the use of a stoichiometric toxic cyanation reagent. The Cu-complex plays a dual role. It is not only a photocatalyst, but also a coupling catalyst for the formation of a C–CN bond.


Abstract: Affinity, which is the essential attribute of metal ions, is very important to their physical and chemical properties. To make quantitative description and deep understanding on the affinity, fourteen metal ions were considered, and two representative ligands (H2O and NH3) were selected. Five types of energy of five models have been calculated using the density functional theory. Then, the results have been applied to quantify the affinity and describe its evolution in the ligand exchange process. Three aspects, energy decomposition analysis, natural bond orbital analysis, and information-theoretic approach in density functional reactivity theory, have been considered to understand the affinity.


Abstract: The development of efficient protocols for the synthesis of gem-difluoroolefins has received increasing attention. Given the ubiquity of hydroxyl group in biologically active molecules and synthetic intermediates,we developed a one-step protocol for the conversions of alcohols into gem-difluoroolefins. The reactions of alcohols with Ph3P+CF2CO2−/Burgess reagent in DMSO occurred smoothly to afford the final products in moderate to high yields. DMSO is not only necessary for the oxidation process,but also important for the stabilization of phosphonium ylide by trapping difluorocarbene.


Abstract: The study of transition-metal difluorocarbene complex has long been a subject of active investigation, but the transition-metal-catalyzed transfer of difluorocarbene remains a significant challenge. The Pd-catalyzed transfer of difluorocarbene is described to realize the coupling reaction of boronic acids with difluorocarbene to give (difluoromethyl)arenes and -olefins. Mechanistic investigations reveal that the Pd═CF2 complex is an important intermediate for this transformation. This complex is prone to trimerization without the presence of starting materials.


Abstract: A convenient method for deoxyfluorination of aromatic and aliphatic carboxylic acids with CF3SO2OCF3 in the presence of a suitable base at room temperature has been developed. The reaction allows a straightforward access to a variety of acyl fluorides and proves that CF3SO2OCF3 is an effective deoxyfluorination reagent for carboxylic acids. The method features simplicity, expeditiousness, high efficiency, ease of handling, good functional group tolerance, a wide range of substrates, excellent yields of products, compatibility of many amine initiators, use of environmentally friendly reagents, and effortless removal of byproducts. This reaction represents the first utilization of trifluoromethyl trifluoromethanesulfonate as a fluorination reagent.


Abstract: A large number of fluorination methods have been developed, but the construction of a tertiary C−F bond remains challenging. Herein, we describe an efficient dehydroxylative fluorination of tertiary alcohols with Selectfluor via the activation of a hydroxyl group by a Ph2PCH2CH2PPh2/ ICH2CH2I system. Although the reagents appear to be not compatible (Selectfluor with the phosphine and I− generated in situ), the reactions occur rapidly to give the desired products in moderate to high yields. This work may present a new discovery in fluorination of alcohols since the reported methods are mainly limited to primary and secondary alcohols.


Abstract: Owing to the special effects of the fluorine element, including high electronegativity and small atomic radius, the incorporation of a fluorinated group into organic molecules may modify their physical, chemical, and biological properties. Fluorine containing compounds have found widespread application in a variety of areas, and thus, the development of efficient reagents and methods for the incorporation of fluorinated groups has become a subject of significant interest. Described in this Account are our recent discoveries in the chemistry of fluorinated ylides/carbenes and related intermediates generated from phosphonium/sulfonium salts. Initially, we obtained the (triphenylphosphonio) difluoroacetate, Ph3P+CF2CO2- (PDFA), which was proposed as a reactive intermediate but had never been successfully synthesized. PDFA, shelf-stable and easy to prepare, is not only a mild ylide (Ph3P+CF2-) reagent, but also an efficient difluorocarbene source. It can directly generate difluorocarbene, via the first generation of ylide Ph3P+CF2-, simply under warming conditions without the need for any additive. Interestingly, difluorocarbene chemistry was then discovered by using PDFA as a reagent. Difluorocarbene can be oxidized to CF2=O, can react with elemental sulfur to afford CF2=S, and can be trapped by NaNH2 or NH3 to give CN-. The development of these processes into synthetic tools allowed us to achieve various reactions, including the challenging 18F trifluoromethylthiolation and cyanodifluoromethylation. It was found that a substituent on the cation of a phosphonium salt can be directly transferred as a nucleophile despite the cation’s high electrophilicity. This transfer process is like an “umpolung” of the cation, which may provide more opportunities for the synthetic utilities of phosphonium salts. The investigation of this transfer process led us to find that iodophosphonium salts, active intermediates which can be easily generated, may efficiently promote deoxygenative functionalizations of aldehydes and alcohols. Dehydroxylative substitution of alcohols by this protocol permits the use of unprotected amines with higher pΚa values as nucleophiles, which is an attractive feature compared with the Mitsunobu reaction. On the basis of the ylide-tocarbene process (Ph3P+CF2- → :CF2), we further developed sulfonium salts as precursors of fluorinated ylides and fluorinated methyl carbenes. In particular, the studies on difluoromethylcarbene, remaining largely unexplored, may deserve more attention. The discoveries may find utility in the synthesis of biologically active fluorine-containing molecules.


Abstract: A large number of trifluoromethylthiolation methods have been developed, but a trifluoromethylthiolation reagent usually has to be used in these methods. Herein we describe a difluorocarbene-based trifluoromethylthiolation of terminal alkynes to construct a Csp-SCF3 bond catalysed by a copper complex. Ph3P+CF2CO2-/S8/F- was used as a reagent system to form the CF3S- anion, and the sequential formation of CF2=S, F-CF2S and C-SCF3 bonds was achieved in a one-step process.


Abstract: We report herein a general and practical coppercatalyzed fluorosulfonylation reaction of a wide range of abundant arenediazonium salts to smoothly prepare various arenesulfonyl fluorides using the 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-bis(sulfur dioxide) adduct as a convenient sulfonyl source in combination with KHF2 as an ideal fluorine source and without the need for additional oxidants. Interestingly, the electronic character of the arene ring in the starting arenediazonium salts has a significant impact on the reaction mechanistic pathway.


Abstract: In order to provide feasible methods for the extraction of valuable metals from spent batteries or low-grade primary ores, the extraction behavior of some representative acidic phosphoruscontaining compounds (APCC) as extractants is evaluated from the perspective of experimental and theoretical investigations in this work. Aqueous solutions containing five metal ions, Ca(II), Co(II), Mg(II), Mn(II), and Ni(II), were made to simulate leaching liquids, and the extraction of these metals were investigated. A simplified calculated model was used to evaluate the interaction between each extractant and metal ions. The calculation results agree well with the experimental tests in trend. This work not only provides potential extractants for the extraction of valuable metals from spent batteries or low-grade primary ores, but also demonstrates the practicability of the simplified calculation model


Abstract: For the dehydroxylation of aldoximes with 4-nitro-1-((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)-imidazole (NTSI), slight modifications of reaction conditions resulted in significantly different reaction paths to provide either nitriles or isonitriles. The challenging conversion of aldoximes into isonitriles was achieved under mild conditions.


Abstract: A large number of efficient cyanation methods have been developed because of the wide range of applications of nitriles, but conventional methods usually suffer from the need for a toxic cyanation reagent. Although difluorocarbene chemistry has received increasing attention, the use of difluorocarbene as a sources of the nitrile carbon for nitrile groups remains largely unexplored. We describe a difluorocarbene based cyanation of aryl iodides promoted by a cheap copper source, Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O, under an air atmosphere. Ph3P+CF2CO2–, an easily available and shelf-stable difluorocarbene reagent, and NaNH2 are used as the carbon source and the nitrogen source for the nitrile group, respectively. The cyanation protocol is attractive because no toxic reagent is used and performing the reactions under an air atmosphere is operationally convenient.


Abstract: CF3S,CF3 and HCF2 groups have been identified as valuable functionalities for drug development. Despite significant accomplishments in the trifluoromethylthiolation,trifluoromethylation and difluoromethylation reactions,directly converting common functional groups into CF3S,CF3 or HCF2 groups are still highly desirable. Described here is the dehydroxylative trifluoromethylthiolation,trifluoromethylation and difluoromethylation of alcohols promoted by a R3P/ICH2CH2I system. All of these dehydroxylative reactions were achieved under mild conditions via the activation of the hydroxyl group by the R3P/ICH2CH2I system. A wide substrate scope and good functional group tolerance were observed.


Abstract: The difluoromethylthio group (HCF2S), which has been identified as a valuable functionality in drug and agrochemical discovery, has received increased attention recently. Two strategies, difluoromethylation and direct difluoromethylthiolation, have been well established for HCF2S incorporation. The former strategy suffers from the need to prepare sulfur-containing substrates. In contrast, direct difluoromethylthiolation is straightforward and step-economic. This short review covers the recent advances in direct difluoromethylthiolation, including electrophilic, radical, and transition-metal-catalyzed or -promoted reactions.


Abstract: Tetrahydropyridinol derivatives were recently reported to exhibit good biological activities,and the incorporation of fluorine into organic molecules may have profound effects on their physical and biological properties. Therefore,we investigated the anticancer activities of six fluorinated tetrahydropyridinol derivatives that we synthesized previously. We found that only one compound,3,3- difluoro-2,2-dimethyl-1,6-diphenyl-5-tosyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-ol,showed significant antiproliferative activity on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 andHMCCLM3cells (the IC50 values were 21.25 and 29.07 μM,respectively). We also found that this compound mediated cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase at 30–40 μM. Western blot analysis demonstrated that the cell cycle arrest induced by this compound in HepG2 andHMCCLM3cells was associated with a significant decrease in Cdc2 and cyclin B1,which led to the accumulation of the phosphorylated-Tyr15 (inactive) form of Cdc2 and low expression of M phase-promoting factor (cyclin B1/Cdc2). Moreover,cells treated with this compound exhibited decreased expression of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)- activating kinase (CDK7/cyclin H). This compound also induced cell apoptosis via activation of caspase-3. A xenograft model in nude mice demonstrated anti-liver cancer activity and the mechanism of action of this compound. These findings indicated that the anticancer effect of this compound was partially due to G0/G1 cell cycle arrest via inhibition of CDK7-mediated expression of Cdc2,and this compound may be a promising anticancer candidate for further investigation.

Abstract: As a versatile intermediate, diflfluorocarbene is an electron-defificient transient species, meaning that its oxidation would be challenging. Herein we show that the oxidation of diflfluorocarbene could occur smoothly to generate carbonyl flfluoride. The oxidation process is confifirmed by successful triflfluoromethoxylation, 18O-triflfluoromethoxylation, the observation of AgOCF3 species, and DFT calculations.

Abstract:Described here is the radical-mediated hydrodifluoromethylation of alkenes that occurs under transition-metal-free conditions by using the phosphonium salt [Ph3P+CF2H]Br- irradiated with a 26 W household compact fluorescent light. The reaction lends itself to a convenient protocol for the installation of a C-CF2H bond while maintaining good functional group tolerance.



Abstract: Photocatalyzed cyanodifluoromethylation of alkenes with a Ph3P+CF2CO2- /NaNH2 (or NH3) system is described. Ph3P+CF2CO2- acted as both the HCF2 source and CN carbon source, and the cyanide anion was generated in situ under mild conditions, avoiding the use of toxic cyanation reagents.



Abstract: As trifluoromethylthiolation has received increasing attention recently, many CF3S-reagents and trifluoromethylthiolation methods have been developed. Herein we describe trifluoromethylthiolation of alkyl halides by using Ph3P+CF2CO2− as a fluoride and difluorocarbene source. Difluorocarbene is a versatile intermediate, but its side reactions are usually ignored and the by-products would therefore be discarded. In this work, a side reaction of difluorocarbene, the generation of a fluoride anion from difluorocarbene, was developed into a synthetic tool. Although the trifluoromethylthiolation reaction involved multi-sequential steps, the cleavage of C–F bond, the formation of CF2=S bond, F-C(S)F2 bond, and C-SCF3 bond, the conversion proceeded fast and was completed within 10 min.

Abstract: Cu-Promoted difluorocarbene-derived trifluoromethylselenolation of benzyl halides with the Ph3P+ CF2CO2/Se/F system is described. Three new carbon–heteroatom bonds, a Se–CF2 bond, SeCF2–F bond, and C–SeCF3 bond, were sequentially formed in the reaction. This work represents the first trifluoromethylselenolation protocol involving an external fluoride for the generation of the key intermediate, CF3Se anion.


Abstract: Wittig gem-difluoroolefination of aldehydes with difluoromethyl phosphonium salt (Ph3P+CF2H•Br-) by using zinc oxide as a base is described. Although the proton in the CF2H group is acidic and a base could easily lead to its deprotonation to form ylide ( Ph3 P CF2 -), the attack of the base at the positive phosphorus atom may also take place to produce a nucleophilic [ HCF2- ] equivalent, and then nucleophilic difluoromethylation instead of Wittig reaction would occur. The use of ZnO as the base favored the Wittig reaction and the nucleophilic difluoromethylation was not observed. Furthermore, the excessive ZnO and ZnII salts produced from ZnO could be easily removed by filtration, which may be convenient for the purification process.

Abstract :Ph3P/I–-promoted dichlorination and dibromination of epoxides by using XCH2CH2X (X = Cl or Br) as the halogen source and reaction solvent is described. All reagents are widely available and easy to handle, and mild conditions and operational simplicity make this protocol attractive.


Abstract: Ag-mediated triflfluoromethylthiolation of inert Csp3−H bond with CF3SOCl is described. Widely available reagents and operational simplicity make this protocol attractive.



Abstract: Although CF3SO2Cl is an efficient chlorotrifluoromethylation reagent, an expensive transition metal complex usually has to be used. We found that CuCl2-catalyzed chlorotrifluoromethylation of alkenes with CF3SO2Cl occurred smoothly under mild conditions. A wide substrate scope and good functional group compatibility were observed.


Abstract: The preparation of highly pure KF-ZrF4 (FKZr) molten salt, a potential secondary coolant in molten salt reactors, was realized simply by heating a mixture of (NH4)2ZrF6 and KF. X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that the FKZr molten salt was mainly composed of KZrF5 and K2ZrF6. The melting point of the prepared FKZr molten salt was 420–422 °C under these conditions. The contents of all metal impurities were lower than 20 ppm, and the content of oxygen was lower than 400 ppm. This one-step protocol avoids the need for a tedious procedure to prepare ZrF4 and for an additional purification process to remove oxide impurities, and is therefore a convenient, efficient and economic preparation method for high-purity FKZr molten salt.


Abstract: Fluoride molten salt has many advantages,such as high temperature stability,high thermal conductivity,large heat capacity,wide electrochemical window,low saturated vapor pressure and small neutron absorption cross section. It is an important functional material which has found widespread applications. The typical preparation and purification methods of fluoride molten salt,including vacuum dehydration,fluorination using ammonium fluoride,H2-HF purification,electrochemical purification and reduction with metals,are introduced in detail. The mechanism and technical characteristics are analyzed for the different methods that are used to remove impure ions in molten salt. At the same time,the applications and progress of fluoride molten salts in nuclear energy,metallurgy, functional materials preparation,advanced energy storage medium,surface treatment technology, electronic chemicals,fine chemicals and molten salt battery materials are reviewed. The fluoride molten salts are mainly used as the nuclear reactor coolant,molten salt electrolyte,high temperature energy storage material and reaction medium. The existing problems in this area are also discussed. It is important to study and clarify the preparation and purification mechanism of fluoride molten salt,toexplore the existence form and impurity migration nature in the process of fluoride purification,and to develop a new method for the purification of the molten salt to reduce its corrosion and cost.

SUMMARY: The CF3O functional group is a unique flfluorinated group that has received a great deal of attention in medicinal chemistry and agrochemistry. However, triflfluoromethoxylation of substrates remains a challenging task. Herein we describe the dehydroxytriflfluoromethoxylation of alcohols promoted by a R3P/ICH2CH2I (R3P = Ph3P or Ph2PCH=CH2) system in DMF. P-I halogen bonding drives the reaction of R3P with ICH2CH2I in DMF to generate iodophosphonium salt (R3P+I I) and a Vilsmeier-Haack-type intermediate, both of which could effectively activate alcohols, thus enabling a fast (15 min) triflfluor omethoxylation reaction. A wide substrate scope and a high level of functional group tolerance were observed.


Abstract:The high demand for the biologically active CF2H-molecules has stimulated significant efforts to develop efficient methods for the installation of CF2H functionality. We found that phenylsulfonyl difluoroacetate salt (PhSO2CF2CO2− K+) could directly undergo decarboxylation under warming conditions to produce active anion (PhSO2CF2−) without the need of any base or additive, thus allowing for the subsequent nucleophilic (phenylsulfonyl)difluoromethylation of aldehydes or imines to give PhSO2CF2-alcohols or -amines, respectively. Interestingly, the removal of PhSO2 group was achieved simply by elevating the reaction temperature for the conversion of aldehydes to afford CF2H-ketones.


Abstract:The Ph3P/ICH2CH2I system-promoted dehydroxylative substitution of alcohols was achieved to construct C–O, C–N, C–S and C–X (X = Cl, Br, and I) bonds. Compared with the previous approaches such as the Appel reaction and Mitsunobu reaction, this protocol offers some practical advantages such as safe operation and a convenient amination process.


Abstract:An efficient reagent system, Ph3P/XCH2CH2X (X = Cl, Br, or I), was very effective for the deoxygenative halogenation (including fluorination) of alcohols (including tertiary alcohols) and aldehydes. The easily available 1,2-dihaloethanes were used as key reagents and halogen sources. The use of (EtO)3P instead of Ph3P could also realize deoxy-halogenation, allowing for a convenient purification process, as the byproduct (EtO)3P═O could be removed by aqueous washing. The mild reaction conditions, wide substrate scope, and wide availability of 1,2-dihaloethanes make this protocol attractive for the synthesis of halogenated compounds.


Abstract:The tri- and di-fluoroethylation of alkenes with sulfonium salts, (Ph2SCH+2RF TfO−) (RF = CF3 or HCF2), by visible light photoredox catalysis to give tri-/di-fluoroethyl alkenes or methoxytri-/di-fluoroethylation products are described. It was found that varying the reaction solvent led to changes in the reaction path.


Abstract:Molecular acidity of trivalent rare-earth metal cations in aqueous solution is an important factor dedicated to the efficiency of their extraction and separation processes. In this work, the aqueous acidity of these metal ions has been quantitatively investigated using a few theoretical approaches. Our computational results expressed in terms of pKa values agree well with the tetrad effect of trivalent rare-earth ions extensively reported in the extraction and separation of these elements. Strong linear relationships have been observed between the acidity and quantum electronic descriptors such as the molecular electrostatic potential on the acidic nucleus and the sum of the valence natural atomic orbitals energies of the dissociating proton. Making use of the predicted pKa values, we have also predicted the major ionic forms of these species in the aqueous environment with different pH values, which can be employed to rationalize the behavior difference of different rare-earth metal cations during the extraction process. Our present results should provide needed insights not only for the qualitatively understanding about the extraction and separation between yttrium and lanthanide elements but also for the prediction of novel and more efficient rare-earth metal extractants in the future.


Abstract:The reaction of thiocarbonyl fluoride, generated from difluorocarbene, with various amines under mild conditions is described. Secondary amines, primary amines, and o-phenylenediamines are converted to thiocarbamoyl fluorides, isothiocyanates, and difluoromethylthiolated heterocycles, respectively. Thiocarbamoyl fluorides were further transformed into trifluoromethylated amines by using a one-pot process. Thiocarbonyl fluoride is generated in situ and is rapidly fully converted in one pot under mild conditions; therefore, no special safety precautions are needed.


Abstract:Dehydroxytrifluoromethylthiolation of alcohols with a Ph3PCF+2CO2–/S8/F–system is described. Difluorocarbene generated from Ph3PCF+2CO2– would readily combine with elemental sulfur to furnish S═CF2. S═CF2 can be considered as a bifunctional intermediate, activating alcohol and providing scaffold for CF3S– formation, thus allowing for the convenient dehydroxytrifluoromethylthiolation of alcohols.


Abstract:The highly diastereoselective synthesis of CF3-containing vicinal diamines by a convenient two-step procedure without the need to isolate the intermediate products is described.


Abstract:The Fe-catalyzed insertion of fluoromethylcarbenes including trifluoromethylcarbene and difluoromethylcarbene generated in situ from sulfonium salts (Ph2SCH+2CF3−OTf and Ph2SCH+2CF2H−OTf) into X–H (X = Si, C and P) bonds is described. The insertion of both carbenes into the Si–H bond occurred smoothly, and trifluoromethylcarbene could also insert into C–H and P–H bonds.


Abstract:The preparation conditions and purification reaction mechanism for H2–HF treatment of molten FLiNaK salt were investigated. The optimal process conditions for preparation of high-purity molten FLiNaK salt were obtained. They are purification temperature of 650°C, liquid height of 0.9m, purification time of 48h, flow ratio of H2/HF = 10, flow volume magnitude of 800 mL/min, and reaction pressure of 0MPa. The oxygen content of the prepared molten salt was around 80 ppm, corrosion impurity elements (Cr, Fe, and Ni) were less than 20ppm, and the S and P contents were below 5ppm. The quality of FLiNaK molten salt prepared by this hydrofluorination process is better than that obtained by adding NH4HF2 as a fluorinating reagent.


Abstract:Difluoroethylsulfonium salt, Ph2SCH+2CF2H OTf−, was developed into a convenient difluoromethylcarbene reagent for the iron-catalyzed cyclopropanation of terminal olefins, giving various difluoromethyl–cyclopropanes with excellent diastereoselectivities and in high yields.


Abstract:Trifluoromethylthiolation by sulfuration of difluorocarbene with elemental sulfur is described for the first time, which overrides long-standing trifluoromethyl anion-based theory. Mechanistic elucidation reveals an unprecedented chemical process for the formation of thiocarbonyl fluoride and also enables transition-metal-mediated trifluoromethylthiolation and [18F]trifluoromethylthiolation of α-bromo carbonyl compounds with broad substrate scope and compatibility.


Abstract:A fluorinated substituent on the positive phosphorus in phosphonium salt [Ph3P+CF(Me)CO2Et Br−] was found to be able to act as a nucleophile to realize monofluoroalkylation of aldehydes, ketones and imines.


Abstract:The fluorinated phosphonium salt (Ph3PCF+2CH3 BF4–) was shown to act as a nucleophilic 1,1-difluoroethylation agent to enable difluoroethylation of aldehydes and imines.


Abstract:The base-free O-difluoromethylation of 1,3-diones with difluorocarbene generated from difluoromethylene phosphobetaine (Ph3P+CF2CO2−) is described. The convenient reactions proceeded smoothly to give difluoromethyl enol ethers in moderate to good yields.


Abstract:Difluoromethylation of N-arylsulfonyl hydrazones with difluorocarbene generated from difluoromethylene phosphobetaine (Ph3P+CF2CO2-) to give various difluoromethyl aryl sulfones is described.


Abstract:Outstanding accomplishments have been achieved in the chemistry of difluorocarbene, but transition‐ metal‐catalyzed transfer of difluorocarbene for coupling remains a challenging task. Herein, we describe a Pd‐catalyzed coupling of difluorocarbene with two aryl carbon centers to give difluoromethylenation products, which cannot be obtained by any previous difluorocarbene‐transformation method.


Abstract:The hydroperfluoroalkylation of electron-deficient olefins with perfluoroalkyl iodides promoted by a zinc/viologen system is described. Interestingly, no iodoperfluoroalkylation product was observed without the presence of radical H-donor.


Abstract:Phosphonium salt ([Ph3P+CF2H] Br–, DFPB) was found to be an efficient nucleophilic difluoromethylation reagent. Although DFPB is known as a phosphonium ylide precursor, its reaction with carbonyl compounds under traditional “Wittig reaction conditions” did not give the expected Wittig difluoroolefinated products, but afforded the nucleophilic difluoromethylation products, α-CF2H alcohols. Mechanistic investigation reveals that the unexpected transformation proceeded via the direct transfer of the CF2H group, which resulted from the high P–O affinity.


Abstract:In this work, the effect of the substituent at the α or β position in dialkylphosphinic acids on the extraction of trivalent lanthanide ions was investigated using experimental and theoretical methods. Five dialkylphosphinic acids were synthesized. Their extractions of seven trivalent lanthanide ions, La/Pr, Nd/Dy, and Ho/Yb/Lu, which represent light, middle, and heavy rare-earth metals, were explored. A simplified coordination model was built to explore the bonding between the extractants and lanthanide ions. The results obtained using this model generally explained the experimental results. The model could therefore be used to study the effects of the α and β substituents of extractants on their extraction properties. The theoretical and experimental results indicate that the significance of a β substituent in the dialkylphosphinic acid on extraction was greater than that of an α substituent.


Abstract:The trifluoromethylcarbene (:CHCF3) was found to be conveniently generated from (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)diphenyl-sulfonium triflate (Ph2S+CH2CF3–OTf), which was successfully applied in Fe-catalyzed cyclopropanation of olefins, giving the corresponding trifluoromethylated cyclopropanes in high yields.


Abstract:Ninety‐six acidic phosphorus‐containing molecules with pKa 1.88 to 6.26 were collected and divided into training and test sets by random sampling. Structural parameters were obtained by density functional theory calculation of the molecules. The relationship between the experimental pKa values and structural parameters was obtained by multiple linear regression fitting for the training set, and tested with the test set; the R2 values were 0.974 and 0.966 for the training and test sets, respectively. This regression equation, which quantitatively describes the influence of structural parameters on pKa, and can be used to predict pKa values of similar structures, is significant for the design of new acidic phosphorus‐containing extractants.

Abstract:The differences of thermodynamics energies from the pure phase to a solution were used to predict the solubility properties of acidic phosphorus–containing rare-earth extractants. Four solvents, namely tributylphosphate, n-dodecane, toluene, and n-octanol were used. The thermodynamic cycle of the implicit solvation model and the structure model with short carbon chains were used. The relationship obtained by simulation of the solubility properties and extractant structures agreed qualitatively with reported experimental results. These results provide guidance for the design of new efficient extractants.

Abstract:DBU‐promoted trifluoromethylation of aryl iodides with difluoromethyltriphenylphosphonium bromide (DFPB) in the presence of copper source is described. In this transformation, DBU not only acts as base to deprotonate the difluoromethyl group in DFPB to generate difluoromethylene phosphonium ylide Ph3P+CF2−, but also converts the difluorocarbene generated from ylide Ph3P+CF2− into trifluoromethyl anion, finally resulting in the trifluoromethylation of aryl iodides. The reactions proceeded smoothly to afford expected products in moderate to good yields.


Abstract:A new method has been developed for the Cu-catalyzed C–H trifluoromethylation of 3-arylprop-1-ynes for the selective construction of allenic Csp2–CF3 and propargyl Csp3–CF3 bonds. The selective formation of allenic Csp2–CF3 and propargyl Csp3–CF3 bonds can be controlled by modifying the reaction conditions.


Abstract:Organic phosphonium salts have served as important intermediates in synthetic chemistry. But the use of a substituent on the positive phosphorus as a nucleophile to construct C–C bond remains a significant challenge. Here we report an efficient transition-metal-free protocol for the direct nucleophilic arylation of carbonyls and imines with tetraarylphosphonium salts in the presence of caesium carbonate. The aryl nucleophile generated from phosphonium salt shows low basicity and good nucleophilicity, as evidenced by the successful conversion of enolizable aldehydes and ketones. The reaction is not particularly sensitive to water, shows wide substrate scope, and is compatible with a variety of functional groups including cyano and ester groups. Compared with the arylmetallic reagents that are usually moisture sensitive, the phosphonium salts are shelf-stable and can be easily handled.


Abstract:The O-difluoromethylation of 1,3-diones with S-difluoromethyl sulfonium salt is described. The sulfonium salt was previously believed to be a direct difluoromethylation reagent, but our mechanistic investigation reveals that the O-difluoromethylation reaction proceeds not only via the direct transfer of the CF2H group, but also via a difluorocarbene process. This work represents the first protocol for mild O-difluoromethylation of acyclic 1,3-diones.


Abstract:(NH4)2BeF4 was synthesized and purified by recrystallization to remove sulfate ions before being used as the main raw material to prepare Li2BeF4 molten salt. (NH4)2BeF4 was heated and melted with LiF at high temperature to produce Li2BeF4 molten salt without separate BeF2 preparation by pyrolysis. The obtained salt has a melting point of 458–460°C and an oxygen content below 500ppm. The main impure metal ion and anion concentrations are less than 10ppm and 80ppm, respectively. This is a convenient, efficient and economical preparative method for high-purity Li2BeF4 molten salt


Abstract:Dialkylphosphinic acids were synthesised by a microwave-assisted method with high yields and wide substrate applicability. A structure–reactivity study indicates that an increase in steric hindrance in the b position led to a decrease of extraction ratio and heavy rare earth element separation activity. A computational study was also conducted to understand the steric effect.


Abstract: Cross-coupling between difluorocarbene and carbene-derived intermediates generated from diazocompounds was developed to give gem-difluoroolefins, which constitutes a fast practical pathway to achieve hindered gemdifluoroolefins. The cross-coupling between difluorocarbene and aryl diazoacetates proceeded smoothly in the presence of a copper source, whereas its coupling with diaryl diazomethanes occurred well under metal-free conditions. A mechanism involving a copper−difluorocarbene complex was proposed.


Abstract:The first trifluoromethylthiolation and [18F]trifluoromethylthiolation of alkyl electrophiles with in situ generated difluorocarbene in the presence of elemental sulfur and external (radioactive) fluoride ion is described. This transition-metal-free approach is high yielding, compatible with a variety of functional groups, and operated under mild reaction conditions. The conceptual advantage of this exogenous-fluoride-mediated transformation enables unprecedented syntheses of [18F]CF3S-labeled molecules from most commonly used [18F]fluoride ions. The rapid radiochemical reaction time (≤1 min) and high functional-group tolerance allow access to a variety of aliphatic [18F]CF3S compounds in high yields.


Abstract: Csingle bondF bond activation of aliphatic fluorides provides new methodologies for synthesis of new fluorinated building blocks as well as versatile non-fluorinated products. This review covers the recent Csingle bondF bond cleavage examples and further transformation of compounds bearing with an aliphatic fluoride, difluoromethylene group or trifluoromethyl groups. The methods to activate a Csingle bondF bond include activation by Lewis acid, Brønsted superacids and hydrogen bonding, and mediation by transition-metals and rare earth metals. Partial reduction of trifluoromethyl group through a single electron transfer (SET) process can provide the compounds with less fluorine. Bases are often used for the elimination of hydrofluoride. SN2′ displacement is also an important method for transformation of monofluorinated, difluorinated and trifluorinated olefins to various synthetically interesting molecules.


Abstract: A new approach for the synthesis of gem-difluorostyrenes from benzyl bromide is described. Quaternization of triphenylphosphine with benzyl bromide to give phosphonium salts, deprotonation of the corresponding phosphonium salts to produce phosphonium ylide, and the subsequent olefination of phosphonium ylide with difluorocarbene generated from difluoromethylene phosphobetaine (Ph3P+CF2CO2−) by decarboxylation can occur smoothly in one-pot, furnishing the final gem-difluorostyrenes in good yields.


Abstract: As both trifluoromethylthio (CF3S) and trifluoromethoxy (CF3O) moieties have proved to be valuable functionalities in pharmaceutical chemistry, trifluoromethylthiolation and trifluoromethoxylation have received a great deal of attention. For the trifluoromethylthiolation reaction, a variety of efficient methods have been developed. Among these methods, C-H trifluoromethylthiolation avoids the need to prefunctionalize substrates, meaning that this straightforward protocol is quite attractive and promising. The first section of this review summarizes recent advances in this field, including Csp3-H, Csp2-H and Csp-H trifluoromethylthiolation and the asymmetric Csp3-H trifluoromethylthiolation reactions. Trifluoromethoxylation with safe trifluoromethoxylation reagents remains a significant challenge. The second section of this review summarizes the recent progress in trifluoromethoxylation reaction.


Abstract: The visible-light-induced photoredox difunctionalization reactions of styrenes with 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-iodoethane under an oxygen atmosphere in the presence of water give γ-trifluoromethyl alcohols. In this radical reaction, the oxygen atom in the product originates from molecular oxygen, and water is shown to be important to promote the reaction.


Abstract: (2,2,2-Trifluoroethyl)diphenylsulfonium triflate was found to be an efficient ylide reagent for the Johnson–Corey–Chaykovsky reaction to afford trifluoromethyl epoxides, cyclopropanes and aziridines. Interestingly, excellent but different diastereoselectivity was observed for these transformations. Both trifluoromethyl epoxides and cyclopropanes were obtained with trans-selectivity, whereas aziridines were obtained with cis-selectivity.


Abstract: A stereoselective N-iminium ion cyclization with allylsilane to construct vicinal quaternary–tertiary carbon centers was developed for the concise synthesis of (±)-cephalotaxine. The current strategy features a TiCl4-promoted cyclization and ring-closure metathesis to furnish the spiro-ring system. The stereochemical outcome in the N-acyliminium ion cyclization was rationalized by the stereoelectronic effect of the Z- or E-allylsilane. Two diastereomers arising from the cyclization were merged into the formal synthesis of (±)-cephalotaxine.




Abstract: Difluoromethylation of the activated X–H bond (X = N, O and S) and aliphatic thiols, and gem-difluorocyclopropenation of alkynes with difluorocarbene generated in situ from difluoromethylene phosphobetaine (Ph3P+CF2CO2−) by decarboxylation occurred smoothly without the presence of any base or other additives.


Abstract: A practical and efficient method for the direct trifluoromethylthiolation of unactivated C(sp3)H bonds by AgSCF3/K2S2O8 under mild conditions is described. The reaction has a good functional-group tolerance and good selectivity. Initial mechanistic investigations indicate that the reaction may involve a radical process in which K2S2O8 plays key roles in both the activation of the C(sp3)H bond and the oxidation of AgSCF3.


Abstract: Difluorocarbene derived from various carbene precursors could be effectively decomposed by 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU). This decomposition process was successfully applied in the subsequent trifluoromethylation of a variety of (hetero)aryl iodides without the addition of an external fluoride ion. Mechanistic investigation revealed the detailed difluorocarbene conversion process in which the decomposed difluorocarbene is finally transformed into a fluoride ion and carbon monoxide.


Abstract: As a well-developed high-temperature heat carrier, FLiNaK molten salt is cheap and thermodynamically stable. It can be used as the second coolant in high-temperature molten salt reactor and solar heat transfer medium. The presence of oxygen greatly influenced the function of the molten salt reactor such as reducing the solubility of nuclear fuel, the precipitation of uranium oxide which would further lead to local overheating of the fuel circuit. However, there are still no general methods for the analysis of trace oxygen in the molten salt now. Based on the application of oxygen analyzer in the determination of trace oxygen in steel industry, we developed a practical method for the measurement of trace oxygen in FLiNaK molten salt. Optimal test conditions including suitable package container and the cracking power 2800 W were established. The relative standard deviations of oxygen were 3.1% and the recoveries were 85%~101%.

Abstract: Tests on rem oval of sulfate radical contained in beryllium hydroxide were conducted with several different methods ,including washing,barium chloride precipitation and a combined method of hydrolysis by sodium hydroxide and precipitation.Results indicated that washing method had the worst effect,resulting in only 50% sulfate radical removed.And the method of barium chloride precipitation brought the content of sulfate radical in beryllium hydroxide remarkably reduced to less than 0.3%,which,however,was put at a disadvantage by its high cost and possibly accompanied pollution problem.By comparison ,the third method of hydrolysis by sodium hydroxide followed by precipitation could reduce the content of sulfate radical from 6.77% to less than 0.020%,with removal rate up to 99.7% .Furthermore ,this method being characterized by low cost and free of secondary pollution,may be of reference for preparation of beryllium hydroxide of nuclear grade purity.

Abstract: AuI/CuI-co-catalyzed tandem 1,3-acyloxy migration/trifluoromethylation reaction of propargyl esters to give α-trifluoromethyl enones in moderate yields and with excellent stereoselectivity is described. It is proposed that the reaction proceeds through the 1,3-acyloxy migration of the propargyl esters catalyzed by AuI to produce an allenic intermediate, followed by its trifluoromethylation to give the final product.


Abstract: Copper-catalyzed tandem trifluoromethylation/cyclization of internal alkynes with Umemoto's reagent leads to 3-trifluoromethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene derivatives in moderate to good yields. The utility of this copper-catalyzed tandem reaction was demonstrated by oxidizing and reducing the trifluoromethylated product to give naphthalene and tetrahydronaphthalene, respectively, and the development of a short route to a trifluoromethylated analogue of Nafoxidine.


Abstract: The past decade has witnessed the significant advances of asymmetric organocatalytic fluorination, monofluoroalkylation, gem-difluoroalkylation, and trifluoromethylation. This digest summarizes the latest progress of these reactions. In the research area of asymmetric organocatalytic fluorination, a new catalysis concept, chiral anion phase-transfer catalysis strategy, has emerged and has proved to be highly efficient. Asymmetric organocatalytic monofluoroalkylation and gem-difluoroalkylation have been much less explored and the Lewis base/acid catalysis has been the most used strategy. Compared with electrophilic trifluoromethylation, nucleophilic trifluoromethylation has been intensively studied in the research field of asymmetric organocatalytic trifluoromethylation.


Abstract: Difluoromethylene phosphobetaine (Ph3P+CF2CO2−, PDFA), a known difluorocarbene reagent, was found to be able to efficiently trifluoromethylate terminal alkynes in the presence of Cu(I) and potassium fluoride. The transformation proceeded smoothly to afford the corresponding trifluoromethylated acetylenes in moderate yields.

Abstract: Salting-out agents, such as NaCl, were often used in solvent extraction in order to adjust distribution ratio. However, the high-concentration salting-out agent and the low-concentration rare earth in extraction phase create extraordinary difficulties to the accurate measurement of the concentration of rare earths due to the serious spectrum interference of salting-out agent itself. The spectrophotometry and ICP-AES were employed as simple and effective methods for the measurement of rare earths. Nevertheless, both methods were easily affected by the salting-out agent in solvent extraction. The influence of NaCl on the spectrophotometry and ICP-AES measurements was investigated in detail. The experiments showed that the accurate measurement of the rare earth was realized through the combination of spectrophotometry and ICP-AES in the presence of NaCl. For the measurement of the light (La, Ce, Pr, Nd) and middle (Sm, Eu, Gd) rare earths, their concentration could be accurately measured by spectrophotometry when the concentration of NaCl was lower than 0.08 mol·L-1 without matrix-matched. The measured value was lower than the real concentration when the concentration of NaCl was higher than 0.08 mol·L-1 without matrix-matched. It was found that in the case of measurement of the heavy rare earths, matrix-matched condition was necessary for both spectrophotometry and ICP-AES methods. The optical method for the measurement of the light (La, Ce, Pr, Nd) and middle (Sm, Eu, Gd) rare earths is that the concentration of sample is diluted to less than 0.08 mol·L-1 and measured by spectrophotometry method. For the measurement of heavy rare earths, ICP-AES method is recommended under matrix-matched condition.

Abstract: A convenient and effective synthesis of various novel beta-perfluoroalkylated subporphyrins has been developed. beta-Trifluoromethylated subporphyrins were efficiently synthesized by the reaction of brominated subporphyrins with FSO2CF2CO2Me/CuI [with or without Pd(dba)(2)]. Potentially valuable beta-perfluoroalkylated, beta-monotetrafluorobenzo, and beta-monotrifluorobenzo subporphyrins were successfully obtained by a modified sulfinatodehalogenation reaction. Photophysical and electrochemical studies on several typical perfluoroalkylated subporphyrins demonstrated that beta-hexakis-trifluoromethylated subporphyrins show an obviously red-shifted UV/Vis absorption band that arises from macrocycle nonplanar distortion induced by trifluoromethyl groups, but this distortion is not so severe as that of the corresponding beta-octakis(trifluoromethyl)meso-tetraphenylporphyrin. This was supported by their redox potential data. In addition, beta-monotrifluorobenzo subporphyrin exhibits a special fluorescence spectrum of vibronic structure.

Abstract: Oxidative coupling of benzylamines to imines by molecular oxygen is efficiently realized in the presence of very low catalyst loadings of Co(II) β-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-meso-tetraphenylporphyrin. Due to the effect of four β-CF3 groups, the catalyst shows good selectivity and very high turnover number. The reaction is easily scaled up and may provide a convenient way to prepare many imines in large scale.


Abstract: A mild method of converting arylamines into perfluoroalkylated arenes is described. Relatively stable RFCu(CH3CN) complexes are used as perfluoroalkylating agents, which react smoothly with arenediazonium salts to produce various perfluoroalkylarenes in good yields. Based on the results of clock trapping experiments with diallyl ether, a radical process might be involved in the reaction.


Abstract: Wittig reaction of aldehydes with difluoromethyltriphenylphosphonium bromide leading to gem-difluoroolefins in moderate yields is described. The reaction displays a good substrate scope including aryl, heteroaryl and α,β-unsaturated aldehydes. Difluoromethyltriphenylphosphonium bromide could be easily prepared and stored for a long time under air atmosphere. The salt exhibits high thermal stability demonstrated by thermogravimetric analysis. Its structure was confirmed by NMR spectroscopy and single crystal X-ray analysis.


Abstract: The preparation conditions and purification reaction mechanism for H2–HF treatment of molten FLiNaK salt were investigated. The optimal process conditions for preparation of high-purity molten FLiNaK salt were obtained. They are purification temperature of 650 °C, liquid height of 0.9 m, purification time of 48 h, flow ratio of H2/HF = 10, flow volume magnitude of 800 mL/min, and reaction pressure of 0 MPa. The oxygen content of the prepared molten salt was around 80 ppm, corrosion impurity elements (Cr, Fe, and Ni) were less than 20 ppm, and the S and P contents were below 5 ppm. The quality of FLiNaK molten salt prepared by this hydrofluorination process is better than that obtained by adding NH4HF2 as a fluorinating reagent.


Abstract: A copper-mediated trifluoromethylation of propargyl acetates with S-(trifluoromethyl)diphenylsulfonium triflate leading to trifluoromethylated allenes in moderate to excellent yields is described.


Abstract: The decarboxylation of potassium 2-pyridinyl sulfonyldifluoroacetate and its subsequent reaction with aldehydes was found to be an efficient approach for the Julia–Kocienski reaction under mild conditions to give gem-difluoro olefins in moderate to excellent yields. Owing to its high stability in the pure state and its easy decarboxylation in polar solvents, potassium 2-pyridinyl sulfonyldifluoroacetate is expected to be an efficient gem-difluoro-olefination reagent.


Abstract: Boron trihalide-promoted ring-opening reactions of gem-difluorocyclopropyl ketones to give the corresponding β-trifluoromethyl ketones and β-halodifluoromethyl ketones were described. It was found that boron trihalides act as both Lewis acids and nucleophiles and the proximal bond prefers to cleave in this transformation.


Abstract: Rhodium-catalyzed allylic C–F bond activation via oxidative addition was found to be a promising approach for the conversion of allylic difluoro-homoallylic alcohols into trisubstituted monofluoroalkenes in good yields with excellent stereoselectivity. The mechanism study shows that C–F bond activation via oxidative addition is involved and PPh3 is responsible for the excellent stereoselectivity.


Abstract: Tetrafluoroethane β-sultone (TFES) has hundreds of useful fluorinating derivatives as reagents. The reactions of TFES with nucleophiles provide a variety of interesting fluoroalkylsulfonic acids and their derivatives, as well as ω-halo-perfluoropentanesulfonyl fluorides. Fluorosulfonyldifluoroacetic acid derivatives such as FSO2CF2COOH, FSO2CF2COOMe, FSO2CF2COOTMS, HCF2SO2R (R = F, OH, OCF2H, OC6H5), ICF2SO2F, and RCF2OCF2CF2SO2F (R = CF2I, CO2Me, CO2Na) are versatile difluoromethylation and/or trifluoromethylation reagents. FSO2CF2COOH, FSO2CF2COOMe, FSO2CF2COOTMS, HCF2SO2R, and ICF2SO2F can effectively incorporate a CF2 group into O H, N H, S H, C C, and C C bonds. HCF2SO2R (R = OH, OCF2H, OC6F5) and FSO2CF2CO2H generate difluorocarbene under acidic conditions, which significantly expanded the scope of the carbene-based difluoromethylation reactions. FSO2CF2CO2Me, FSO2CF2I, and RCF2OCF2CF2SO2F (R = CF2I, CO2Me, CO2Na) are powerful trifluoromethylation reagents, with FSO2CF2CO2Me being world-renowned and widely used in the design of drug candidates and synthesis of novel functional materials. FSO2CF2CO2Me, FSO2CF2I, and RCF2OCF2CF2SO2F are generally produced by nucleophilic substitution, thermal decomposition, or single-electron transfer mechanism in trifluoromethylation reactions under mild conditions. FSO2CF2CF2OCF2CO2Me can successfully trifluoromethylate unactivated aryl chlorides with CuI, and FSO2CF2CF2OCF2CO2K/CuI can smoothly transform aryl halides at very low temperature. For more than half a century's development, the chemistry of TFES and its derivatives has been extensively studied. This review recounts the recent progress of TFES and reports on TFES-derived difluoromethylation and trifluoromethylation reagents. The syntheses and reactivities of these interesting reagents, as well as their applications in medicinal chemistry and materials science, are briefly summarized.


Abstract: We have developed an efficient method to achieve N-gem-difluorocyclopropylation of N-heterocycles with the use of gem-difluorocyclopropyl tosylate as a building block under mild conditions. gem-Difluorocyclopropyl tosylates could be easily prepared on a large scale and exhibit great stability.


Abstract: CF3-containing esters smoothly reacted with electron-deficient alkenes in the presence of a phosphine (2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2′,4′,6′-triisopropylbiphenyl) organocatalyst at room temperature in an aerobic atmosphere. These Michael reactions efficiently provided products with a CF3 quaternary carbon center.


Abstract: X(CF2CF2)nOCF2CF2SO2F (X=I, Br, Cl; n=1, 2, 3, 4) are widely used fluoroalkylation reagents, which can incorporate ‘heavy’ fluorous tags into organic compounds. X(CF2CF2)nOCF2CF2SO2F have both sulfonyl and halo groups. They behave as bi-functional fluoroalkylation reagents. The cleavage of the C–I bonds of I(CF2CF2)nOCF2CF2SO2F by reductants (such as Na2S2O4, Zn), single electron transfer reagents and radical initiator systems (like Bz2O2, AIBN, and (t-BuO)2, or under UV and heat) gives, respectively, the sulfinatodehalogenated products, the hydrodehalogenated products, the homo-coupling products and the perfluoroalkylated products (if alkenes, alkynes or arenes were added). The functionalization of the sulfonyl groups (SO2F) of X(CF2CF2)nOCF2CF2SO2F by esterification, amidation, and fluorination affords the corresponding perfluoroalkanesulfonates, fluoroalkanesulfonamide, and perfluoroalkanes. In many cases, both the halo and sulfonyl groups of X(CF2CF2)nOCF2CF2SO2F are transformed. These transformations finally lead to hundreds of useful highly fluorinated materials, such as supper acids, catalysts, surfactants, ion-exchange resins, electrolytes, polymers, and dense ionic liquids. Furthermore, X(CF2CF2)nOCF2CF2SO2F have commendable advantages, such as the easy preparation, the wide range of substrate tolerance, the mild reaction condition, and the high yields of desired products, which make them very promising. This review briefly summarizes the synthesis, reactivity, and applications of these intriguing reagents.


Abstract: An efficient method for the copper-catalyzed trifluoromethylation of terminal alkenes with an electrophilic trifluoromethylating reagent has been developed. The reactions proceeded smoothly to give trifluoromethylated alkenes in good to excellent yields. The results provided a versatile approach for the construction of Cvinyl–CF3 bonds without using prefunctionalized substrates.


Abstract: The chloroacetic acid/sodium hydroxide buffer system was applied in the determination of rare earth by photometric analysis. With Arsenazo III as chromogenic reagent, the sensitivity of various buffer systems was explored, including chloroacetic acid/sodium hydroxide, formic acid/sodium hydroxide and acetic acid/sodium acetate. The optimal conditions for the determination of lanthanide ions in chloroacetic acid were found and the corresponding molar absorptivities, were calculated. The results of photometric analysis which can be determined simply and quickly, were agree with the data of ICP-AES.

Abstract: The interconversion between difluoromethylene ylide and difluorocarbene is described. The difluoromethylene ylide precursor, Ph3P+CF2CO2−, could be turned into an efficient difluorocarbene reagent, whereas the classical difluorocarbene reagents, HCF2Cl and FSO2CF2CO2TMS, could generate highly reactive difluoromethylene ylide. Thus the Wittig difluoro-olefination and difluorocyclopropanation could be selectively realized by using the same reagent. In addition, the ylides obtained from different carbene sources showed different reactivity in Wittig reactions.


Abstract: TheCF3SO3H-promoted ring opening of gem-difluorocyclopropyl ketones prefers to undergo proximal bond cleavage and the subsequent cyclization with nitriles occurred smoothly to give 2-fluoropyrroles.


Abstract: A key intermediate, difluoromethylene phosphobetaine, in the Wittig reaction of ClCF2CO2Na–Ph3P with aldehydes was synthesized and characterized, which confirmed the reaction mechanism. The decarboxylation of this stable intermediate was a convenient approach for Wittig difluroolefination. Its reactivity could be adjusted by the modification of the substituent on the phosphorus.


Abstract: The copper-mediated trifluoromethylation of terminal alkynes with S-(trifluoromethyl)diarylsulfonium salt has been carefully investigated. The reactions proceeded smoothly to afford trifluoromethylated acetylenes in moderate to good yields. This approach is a convenient method to synthesize a variety of functional trifluoromethylated acetylenes.

Abstract: Well-defined polystyrene-co-poly(2, 3, 4, 5, 6-pentafluoro styrene) (PS-co-PPFS) copolymers were synthesized by atomic transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) in trifluorotoluene, fluorinated ionic liquid and trifluorotoluene/fluorinated ionic liquid solvent systems, respectively. The chain structure and component of such copolymers were characterized by 1H NMR, 19F NMR, elemental analysis and GPC. Porous films of PS-co-PPFS copolymers were fabricated by static breath-figure method in CS2, CHCl3 and CH2Cl2, respectively. The morphologies of such porous films were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and compared with those of PS homopolymer with similar molecular weight. The results showed that PS-co-PPFS copolymers with narrow molecular weight distribution (Mn=5200~7900 g • mol-1, Mw/Mn= 1.12~1.22) can be synthesized via ATRP in trifluorotoluene and fluorinated ionic liquid, respectively. The SEM observation indicated that PS-co-PPFS copolymer porous films can be fabricated with CS2, CHCl3 and CH2Cl2 as solvent, respectively. While, different from PS analogues, PS-co-PPFS copolymer porous films showed less ordered pore structures with two different average pore sizes. The pores of such film fabricated in CHCl3 were in better order with two average pore sizes of 0.75 and 0.37 μm, respectively.

Abstract: A strategy for building coordination cages by a [6 + 8] condensation of MII4-calix SBUs and rigid ancillary ligands was successfully applied to a cobalt–sulfonylcalix[4]arene system. A giant cage obtained with BTE ligands has an overall periphery diameter of 5.0 nm and an internal spherical cavity of 2.3 nm.


Abstract: An organocatalytic asymmetric method for the synthesis of 2-CF3 tetrahydroquinoline has been achieved. The cascade reaction of 2-aminochalcones with β-CF3 nitroalkenes afforded the products bearing three contiguous stereogenic centers in good yields with excellent diastereoselectivities and enantioselectivities.


Abstract: The sulfinatodehalogenation reaction represents one of the most important methodologies to incorporate fluorine into organic molecules. Using inexpensive sulfur-containing reactants such as Na2S2O4 under mild conditions, per- and polyfluoroalkyl halides (RFX, X = Br, I, CCl3) can be transformed smoothly into the corresponding sulfinate salts. This method is also used for the perfluoroalkylation of alkenes, dienes, alkynes and aromatics. Notably, after 1998, the sulfinatodehalogenation of perfluoroalkyl chlorides (RFCl) has been realized by using dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) as a solvent instead of CH3CN/H2O in the Na2S2O4/NaHCO3 initiation system. Perfluoroalkyl chlorides, ethyl chlorofluoroacetates and chlorodifluoroacetates, and even nonfluorinated compounds, such as ethyl chloro- or dichloroacetates and chloroform, were either converted into the corresponding sulfinate salts or alkylated alkenes, alkynes and aromatics (including porphyrins). The sulfinatodehalogenation reaction has remarkable advantages. With the increasing demands to utilize the unique properties of fluorine and fluorinated functional groups in medicinal, agricultural and material sciences, we believe that there will continue to be useful developments in sulfinatodehalogenation chemistry and it will be applied more widely in the future.


Abstract: Experimental studies showed that Ni(II) N-confused porphyrins, treated with fluoroalkylarylsulfonium salts, can undergo an electrophilic fluoroalkylation at the inner 21-C position, leading to 21-fluoroalkylated Ni(II) N-confused porphyrins.


Abstract: 1-Alkyl-3-methylimidazolium fluorides were successfully synthesized by the reaction of silver fluoride with the corresponding imidazolium iodides.


Abstract: Aldol reaction between simple benzaldehydes and ketones successfully happened in solvent- and catalyst-free condition. The desired products were obtained in moderate yield at suitable temperature. Heat was assumed as the driving force for the reaction. This approach has obvious advantages to fully meet the requirement of the principles of green chemistry.

Abstract: The enantioselective Friedel–Crafts fluoroalkylation of indoles with fluoroalkylated nitroalkenes, catalyzed by chiral phosphoric acid is described. The regioselectivity of fluoroalkylated nitroalkenes is a problem worth discussing, and it was found that the carbon atom adjacent to the fluoroalkyl group is more reactive than that adjacent to NO2 group.


Abstract: The ligand-free trifluoromethylation of arylboronic acids with a [Ph2SCF3]+[OTf]−/Cu(0) system has been carefully investigated. Aryl-, alkenyl- and heteroarylboronic acids with a variety of functional groups were suitable substrates for this reaction. It is suggested that a CuCF3 species is formed under the reaction conditions.


Abstract: Chiral N-heterocyclic carbene catalyzed annulations of ynals and enals with 1,3-dicarbonyls have been described. The two reactions provided direct and efficient methods for enantioselective synthesis of functionalized dihydropyranones. Comparatively, the reactions starting from ynals were atom-economical; furthermore the reactions of enals demonstrated broader substrate compatibility.


Abstract: The CF3 radical was generated from the reaction of S-(trifluoromethyl)diphenylsulfonium triflate with Na2S2O4 or HOCH2SO2Na under suitable conditions without further reduction. Based on this, a method for the synthesis of α-trifluoromethylated ketones has been successfully developed.


Abstract: We thank the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Hundreds of Talents Program), the National Natural Science Foundation (20972179, 21032006), Merck Research Laboratories, and the Syngenta PhD Studentship Award for financial support. We thank Dr. John Clough of Syngenta at Jealott’s Hill International Research Centre and Dr. Shubin Liu of University of North Carolina for proofreading of the manuscript.


Abstract: Monofluorovinyl tosylate was developed as a practical vinyl fluoride building block to couple with a variety of arylboronic acids in the presence of a palladium catalyst. The high stereoselectivity of 2-aryl-1-fluoroethene derivatives was achieved. This approach is also applicable to the synthesis of 2,2-diaryl-1-fluoroethenes in good yields.


Abstract: Both experimental and computational approaches have been employed in the present work to investigate the thermal conversion of substituted difluoro(methylene)cyclopropanes (F2MCP) E-1,1-difluoro-2,2-dimethyl-3-tosylmethylene cyclopropane 1, to the thermodynamically more stable F2MCP products, 1,1-difluoro-2-tosyl-3-(propan-2-ylidene)cyclopropane 2, and 1-(3-(difluoromethylene)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropylsulfonyl)-4-methylbenzene 3. The X-ray crystal structure has been obtained for both 1 and 2, respectively, based on which theoretical analyses on their structure and stability have been carried out. Possible reaction mechanisms are proposed.


Abstract: A series of new bis(fluoroalkanesulfonyl)imide based ionic liquids were synthesized in a one-pot procedure. These ionic liquids have high density, low glass transition temperature and high decomposing temperature, indicating a wide range of liquid state.

Abstract: The N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed reaction of alkynyl aldehydes with 1,3-keto esters or 1,3-diketones has been studied. This protocol offers an entirely new, mild and atom-economical access to highly functionalized 3,4-dihydropyranones.


Abstract: A series of bis(fluoroalkanesulfon)amides were synthesized in good yield from the reaction of fluoroalkanesulfonamides and fluoroalkylsulfonyl fluorides. Ionic liquids based on these amide anions and an imidazolium cation demonstrated high densities and a wide temperature range for the liquid state.


Abstract: Experimental studies demonstrated that alcohols and amines can undergo a CF3COOAg-catalyzed nucleophilic addition at the outer C═N position of Ag(III) NCPs, leading to C-3-alkoxylated Ag(III) NCPs, which supports the computational result that the C═N bond on the periphery of Ag(III) NCPs is partially isolated from the 18 π-electron macrocyclic conjugation system and is the active electrophilic center.


Abstract: The pKa values of a series of fluoroalkanesulfonylamides were measured by potentiometric titration. Different kinds of alkyl halides and tosylates were employed to investigate the nucleophilicity of fluoroalkanesulfonylamides. Fluoroalkanesulfonylamides with longer fluoroalkyl chain have weaker nucleophilicity.


Abstract: S-(fluoroalkyl)diphenylsulfonium salts have been successfully synthesized from the reaction between fluoroalkylsulfinates and triflic anhydride in dichloromethane through a one-pot procedure. These S-(fluoroalkyl) diphenylsulfonium salts have been demonstrated to be effective reagents to fluoroalkylate C-nucleophilic substrates. Ionic substitution and radical or halogenophilic mechanism might be all involved in the reactions.

Abstract: Arylfluoroalkylsulfoxides were successfully synthesized in one-pot when fluoroalkylsulfinate reacted with benzene and triflic anhydride in triflic acid and dichloromethane as the medium. The characteristics of their 19F NMR spectra were examined and analyzed for these structures. Electronic and steric effects of substituents at α- or β-position were revealed to be the main cause of the anomalous behavior of their chemical shifts and coupling constants. Interactions between arylfluoroalkylsulfoxides and solvents were also investigated and discussed.

Abstract: Since the first synthesis of tribenzosubporphyrine in 2006, the chemistry of subporphyrins has attracted great interest. Recently, many methods have been developed to synthesize multiple-substituted subporphyrins. It is notable that the preparation of subporphyrin through the metathesis of expanded porphyrin is an effective way. Subporphyrin possesses a 14π conjugation system and C 3 symmetric bowl arrangement. The properties of subporphyrins such as UV-Vis spectra, fluorescence and substituent effects, are much different from those of normal porphyrins, which can be well explained by a four obital model, theoretical calculations and X-ray single crystal analysis. The subporphyrins bearing large meso-aryl groups exhibited some interesting properties including higher energy transfer efficiency, enhanced fluorescence intensity and two-photon absorption. Such modified subporphyrins have great potential applications to electronics and optics.

Abstract: Water was found to be a suitable reaction medium for the direct asymmetric aldol reaction of various cyclic ketones with aryl aldehydes catalyzed by a primary-tertiary diamine-Brønsted acid.


Abstract: A new precursor of N-heterocyclic carbene bearing push-pull substituents has been synthesized by the quaternization of 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-imidazole. Unexpected reactions between the carbene generated in situ and aromatic aldehydes or acrylates were observed resulting in the formation of imidazole derivatives.


Abstract: Difluorocarbene generated from FSO2CF2CO2SiMe3 (TFDA) at 120 °C could reacted with terminal alkynes having an ester group at the α position to the triple bond. Difluorocyclopropenes were further converted to difluorocyclopropyl ketones under alkaline condition. Mechanism for the conversion was studied.


Abstract: A mild hydrodehalogenation reaction of fluoroalkyl halides (RfCF2X, X = Br, I) has been developed under weakly basic conditions, giving the corresponding hydrogenolysis products with moderate to high yields.


Abstract: The oxidation of Ni(II) N-confused porphyrins (NCPs) with azo radical initiators resulted in an unexpected intramolecular nucleophilic substitution reactionvia a proposed Ni(III) NCP intermediate, which could be detected by HRMS.


Abstract: A series of pyrrolidinium-based salts with new fluorine-containing anions were synthesized. Different melting points could be obtained by changing the length of the fluoroalkyl chain of the anions. The pyrrolidinium 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoro-2-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)ethanesulfonate ([C4H8NH2][H(CF2)4O(CF2)2SO3]) is highly fluid even below room temperature. It can be used both as a recyclable solvent and as an efficient catalyst for Friedel–Crafts alkylations of indoles with nitroalkenes.


Abstract: An efficient method was developed for the synthesis of pentafluoroiodoethane from chloropentafluoroethane. Sulfinatodechlorination of CF3CF2Cl was carefully investigated. Subsequent iodination can be conducted in one pot without further purification, giving the corresponding CF3CF2I in practically acceptable yield.


Abstract: The first fluoroalkylated Ni(II) N-confused porphyrins were synthesized with high regioselectivity and its further alkylation was studied.


Abstract: The distal and proximal bond of difluoro(methylene)cyclopropanes (F2MCPs) could be cleaved, respectively, under different conditions to give the corresponding ring-opening products. The reaction mechanisms are discussed.


Abstract: We synthesized several novel low-melting ionic salts with donor–acceptor substituents and investigated their possible applications as second-order nonlinear optical materials.


Abstract: Difluoro-substituted spirocyclopropaneisoxazolidines were formed by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of difluoro(methylene)cyclopropanes (F2MCPs) with nitrones in high yields. The [3+2]-cycloaddition reactions exhibited good regioselectivity and high stereoselectivity. The cycloadducts could rearrange further to form highly substituted 3,3-difluorinated tetrahydropyridinols


Abstract:Hexamethylphophoramide (HMPA) reacted with hexafluorobenzene and its derivatives with good conversion to give dimethylaminated products and phosphorofluoridates, even in unfavorable reaction stoichiometries. An aromatic nucleophilic mechanism might be involved.


Abstract:The Diels–Alder reactions of difluoro(methylene)cyclopropanes (F2MCPs) with cyclic dienes are described. These cycloaddition reactions exhibited complete regioselectivity and high endo-stereoselectivity. The obtained cycloadducts underwent a retro-Diels–Alder reaction to give the original dienophiles and dienes when heated, reflecting the reversible Diels–Alder reactivity of F2MCPs.


Abstract: A new class of geminal dicationic ionic liquids was formed with a bridging moiety, such as a polyalkyl ether, polyfluoroalkyl, 1,4-bismethylenebenzene, or 1,4-bismethylene-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzene link, between alkyl-substituted imidazolium rings. Their properties were modified by varying the linker chains and/or alkyl substituents on the imidazolium ring. The polyfluoroalkyl bridged dicationic ionic liquids exhibit the highest densities and viscosities. Although melting points are directly proportional to the length of the alkyl substituent, the densities decrease concomitantly. With 1,4-bismethylene-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzene as the linking chain and with longer alkyl substituents on the imidazolium rings, the nonpolar character of the ionic liquid greatly increases, e.g., the solubilities in toluene of dicationic ionic liquids 36 and 37, where the ring substituents are C10H21 and C14H29, increase markedly. Some of the salts exhibit higher conductivities than an equimolar tetrabutylammonium iodide solution in acetonitrile/toluene. These new ionic liquids (except with PF6− as anion) display outstanding tribological properties in temperature ramp tests by performing very well at 300 °C, thus meeting one criterion for high-temperature lubricants.


Abstract: 2,4,5-Trinitroimidazolate (TNI) salts with “high-nitrogen” cations tend to be highly hydrogen bonded and have heats of formation ranging up to 616 kJ mol−1. Density, oxygen balance, and thermostability are enhanced by the presence of TNI. Based on theoretical calculations, all of the new salts are potential propellants.


Abstract: The reactions of 2-(2-pyridyl)imidazole with alkyl iodides at 25 degrees C in the presence of base gave rise to 1-alkyl-2-(2-pyridyl)imidazole. Subsequent neat reactions with alkyl or polyfluoroalkyl halides at 100 degrees C, followed by anion exchange with LiN(SO(2)CF(3))(2), generated the mono-quaternary ionic liquids. All of them have excellent thermal stability and wide liquid range. Most of the salts with asymmetric N-substituents are liquid at room temperature. The effect of N-substituent variation and symmetry on NMR, TGA and DSC is discussed. Reaction of with palladium(II) chloride produced a mononuclear palladium ionic liquid complex, the structure of which was confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The Heck cross-coupling reactions using in ionic liquid demonstrated excellent stability and recyclability.


Abstract: A basic ionic liquid was selected to serve as both the solvent and base for Heck, “copper-free” Sonogashira reactions, and for homocoupling reactions of terminal alkynes. The ionic liquids with tertiary aliphatic amines are effective solvents for these reactions. Under reflux conditions, eight equivalent basic ionic liquids and Pd(OAc)2 in THF or acetone produced palladium colloids with diameters of (2.6 ± 0.3) or (3.7 ± 0.5) nm, respectively. Preliminary results for Knoevenagel condensations are also reported.(© Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, Germany, 2007)


Abstract: A series of fluorinated meso,β-fused 5,15-diphenylporphyrins have been synthesized by the reaction of 5,15-diphenylporphyrins with fluoroalkyl halides under modified sulfinatodehalogenation reaction conditions through radical cyclization.

Abstract: Difluoro(methylene)cyclopropanes (F2MCPs) were prepared directly by difluorocarbene addition to allenes,and the resulting F2MCPs were converted into a variety of difluoro(methylene)cyclopropane derivatives through Heck reactions and electrophilic substitutions. The ring-opening reactions of F2MCPs with I2 are reported and a plausible reaction mechanism is also discussed. (© Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA,69451 Weinheim,Germany,2006)


Abstract: We report three crystal structures of a synthetic 5-fluoroalkylporphyrin molecule that was programmed for self-assembly. All the X-ray structures of zincated and free-base porphyrins Zn2 b, Zn5 a, and 2 b revealed rigorous π–π stacking and extremely hydrophobic interactions. Other the other hand, the strong aggregation of 5-fluoroalkylporphyrins in solution was also found. Interestingly, the regular nanopore formation of the 5-fluoroalkylporphyrin was visualized by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Importantly, the 5-fluoroalkylporphyrins possess liquid-crystalline properties that were confirmed by using a combination of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and polarizing optical microscopy (POM) techniques. By comparison, the self-assembly of non-fluorine-containing porphyrins with similar structure showed much lower aggregation ability, as investigated by NMR techniques. Additionally, no birefringent mesophase was observed for the non-fluorine-containing porphyrin.

Abstract: A series of 10,20-diaryl-5-[(E)-fluoroalkenyl]-15-(fluoroalkyl)porphyrins has been synthesized by the reaction of free-base 5,15-diarylporphyrins with fluoroalkyl iodides in the presence of Na2S2O4. Subsequent intramolecular cyclization of the corresponding (fluoroalkenyl)porphyrins occurs smoothly in refluxing toluene/H2O. (© Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, Germany, 2006)


Abstract: In the presence of sodium dithionite and DMSO, the intramolecular radical cyclization of 4-chloro-1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4-octafluorobutylbenzenes is achieved to give the corresponding cyclic compounds in moderate to good yields.


Abstract: A new room-temperature ionic liquid has been synthesized from 2,2'-bipyridine. This liquid improved the copper-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions between perfluoroalkyl or pentafluorophenyl halides and aryl iodides. Good recyclability using this solvent system was observed.


Abstract: Energetic ionic salts of azotetrazolate (AT), iminobis(5-tetrazolate) (IBT) and 5, 5′-bis(tetrazole) (BT) were synthesized; 1-methyl-4-aminotriazolium azotetrazolate has a layered structure and exhibits a heat of formation of +4360 kJ kg−1.


Abstract: Neat reactions of 2,2‘-biimidazole with an excess of alkyl or polyfluoroalkyl iodides at 140 °C, followed by anion exchange with LiN(SO2CF3)2 or KPF6, gave the diquaternary salts 3a−k in >80% yields. However, by controlling the reaction stoichiometry, 2,2‘-biimidazole can also be monoquaternized with the same electrophiles at 100 °C under similar conditions. Subsequent metathesis reactions with LiN(SO2CF3)2 or KPF6 resulted in the ionic liquids 4a−m in high yields. Thermal properties were determined with a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA). Most of the monoquaternary salts are room-temperature ionic liquids. 1,3,1‘-Tributyl-2,2‘-biimidazolium hexafluorophosphate was demonstrated to be an excellent solvent and ligand for palladium-catalyzed Suzuki cross-coupling reactions. The catalytic ionic liquid system may be recycled at least 14 times without a significant decrease in catalytic performance.


Abstract: A microwave-assisted fluorination method for 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds using Selectfluor® has been developed. 2-Monofluorinated products can be obtained in high yield in neutral reaction conditions with addition of 1 eq. of Selectfluor®. Treatment of 1,3-dicarbonyls with 3 eq. of Selectfluor® in the presence of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide (TBAH) as the base results in the formation of 2,2-difluorinated derivatives only.


Abstract: The monoquaternary product of 2,2‘-biimidazole with iodobutane is an ionic liquid that acts as both the solvent and ligand for catalytic reactions. A new palladium complex was prepared by adding PdCl2 to this ionic liquid to form a catalytic solution that is effective for Heck reactions with good recyclability.


Abstract: Treatment of difluorodiiodomethane with TV-sodium salts of imidazoles at - 15 °C gave N-difluoroiodomethylated imidazoles (3) in good yields. The addition of 3 to alkyne or alkenes initiated by sodium dithionate at room temperature resulted in the corresponding adducts in high yields.

Abstract: Treatment of tetrafluoroallene or its precursor,ICF2CH2CF2I,with phenols in the presence of K2CO3 gave the corresponding unsaturated ethers. Tetrafluoroallene also reacted readily with amines in THF at room temperature to afford 3,3,3-trifluoropropionamides.

2. Xiao, Ji-Chang; Chen, Qing-Yun*. “The chemistry of tetrafluoroallene: one-pot synthesis of (trifluoromethyl)indolizines from 1,3-diiodo-1,1,3,3-tetrafluoropropane by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition” Chin. J. Chem. 2003, 21, 898-903.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.20030210735

Abstract: Heating a mixture of 1,3-diiodo-1,1,3,3-tetrafluoropropane (2),K2CO3,pyridinium bromides (3) in CH3CN at 65°C for 10h gives the corresponding trifluoromethylindolizines.

Abstract: Difluorodiiodomethane is prepared in 60% yield by the reaction of difluoro(fluorosulfonyl)acetyl fluoride with I2/KI in the presence of a catalytic amount of SiO2 in acetonitrile at 60-65°C